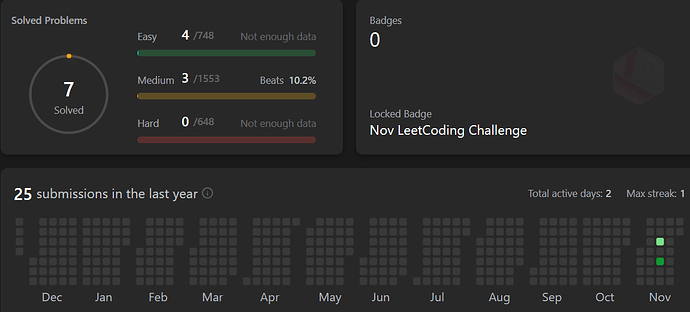
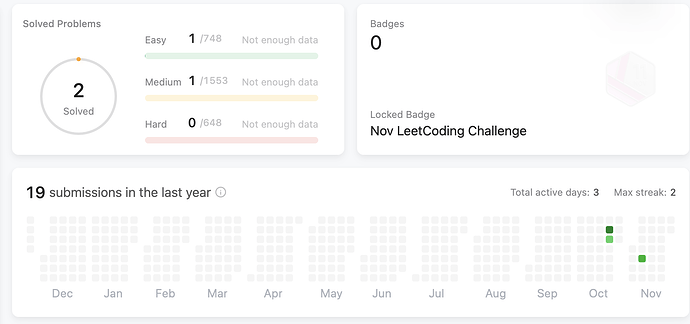
从零开始,此前没有任何算法竞赛经验,没有系统刷过题
「いいね!」 4
加油!楼主要坚持啊,暑假一起刷(
データ構造とアルゴリズム、スタート!
暑假?
今晚蒜了。因为刚刚突然在群里聊嗨了一直聊到现在。
良好的开始![]() 加油捏,寒假一起刷:rofl_kissing_heart:
加油捏,寒假一起刷:rofl_kissing_heart:
时间挤不出来一点![]()
太吊了。一个 easy 也不会
完成しました。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null && slow != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
この問題は少し難しいです。空間複雑度を O(1) にする必要があり、かつリンクリストを modify してもいけません。そこで討論区を確認したところ、実際に難しい問題でした。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null && slow != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
while (slow != head) {
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return head;
}
}
return null;
}
}
「いいね!」 2
ちょっと面白いことに、この medium の問題の答えはたった一行で済む:
class Solution {
public boolean stoneGame(int[] piles) {
return true;
}
}
主な論拠は以下の通り:piles.length が偶数なので、Alice は毎回奇数位置の石か偶数位置の石のどちらかを選択できるが、Bob は選択権がない。もし奇数位置の石の合計が偶数位置の合計より大きいなら、Alice は毎回奇数インデックスの石を取り、Bob は毎回偶数インデックスの石しか取れないため、Alice が常に勝つ。そしてその逆も然り。
「いいね!」 1
草,我 142 第一次做的太直接了,但是还好能 ac(
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode detected = head;// 要被判断是否是开始循环的结点
while (detected != null) { // 下同 141 题 判断是否有循环
ListNode slow = detected;
ListNode fast = detected;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 同时判断是否回到要被判断的结点
if (slow == detected || fast == detected) {
return detected;
}
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
detected = detected.next;
}
return null;
}
}
然后喜提速度最慢一档。后看了讨论区的方法,服了
時間と空間のトレードオフです。空間のために時間を多く犠牲にするよりも、マーク(フラグ)を設ける方がマシです。
(このアルゴリズムの最悪時間複雑度は O(N^2) になる気がする)
「いいね!」 1
毎日一問です ![]()
また無意味な問題だ
class Solution {
public String intToRoman(int num) {
StringBuilder roman = new StringBuilder();
if (num / 1000 > 0) {
roman.append("M".repeat(num / 1000));
num %= 1000;
}
if (num >= 900) {
roman.append("CM");
num -= 900;
}
if (num >= 500) {
roman.append("D");
num -= 500;
}
if (num >= 400) {
roman.append("CD");
num -= 400;
}
if (num / 100 > 0) {
roman.append("C".repeat(num / 100));
num %= 100;
}
if (num >= 90) {
roman.append("XC");
num -= 90;
}
if (num >= 50) {
roman.append("L");
num -= 50;
}
if (num >= 40) {
roman.append("XL");
num -= 40;
}
if (num / 10 > 0) {
roman.append("X".repeat(num / 10));
num %= 10;
}
if (num >= 9) {
roman.append("IX");
num -= 9;
}
if (num >= 5) {
roman.append("V");
num -= 5;
}
if (num >= 4) {
roman.append("IV");
num -= 4;
}
if (num > 0) {
roman.append("I".repeat(num));
}
return roman.toString();
}
}
もちろんこの実装は最適化できる。
「いいね!」 1
デバッグにはお金がかかります、全滅です。
参考 OI wiki の復習で、ハッシュテーブルの衝突処理方法としてアルゴリズムコンテストでよく用いられるのは separate chaining だとわかりました。
「いいね!」 1
本当に成功しました。完全に成功しました。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
Map<Integer, Integer> m = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (m.containsKey(target - nums[i])) return new int[] {i, m.get(target - nums[i])};
m.put(nums[i], i);
}
return null;
}
}
「いいね!」 1